Contents
- 1 Fat Accumulation in the Liver Without Alcohol: A Growing Concern
- 2 Lack of Awareness Delays Treatment
- 3 NAFLD: The Silent Killer
- 4 Understanding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
- 5 Why is NAFLD Prevalent in India?
- 6 Consequences of Fatty Liver Disease
- 7 How to Prevent and Manage NAFLD
- 8 Recognizing the Symptoms of NAFLD
- 9 Conclusion
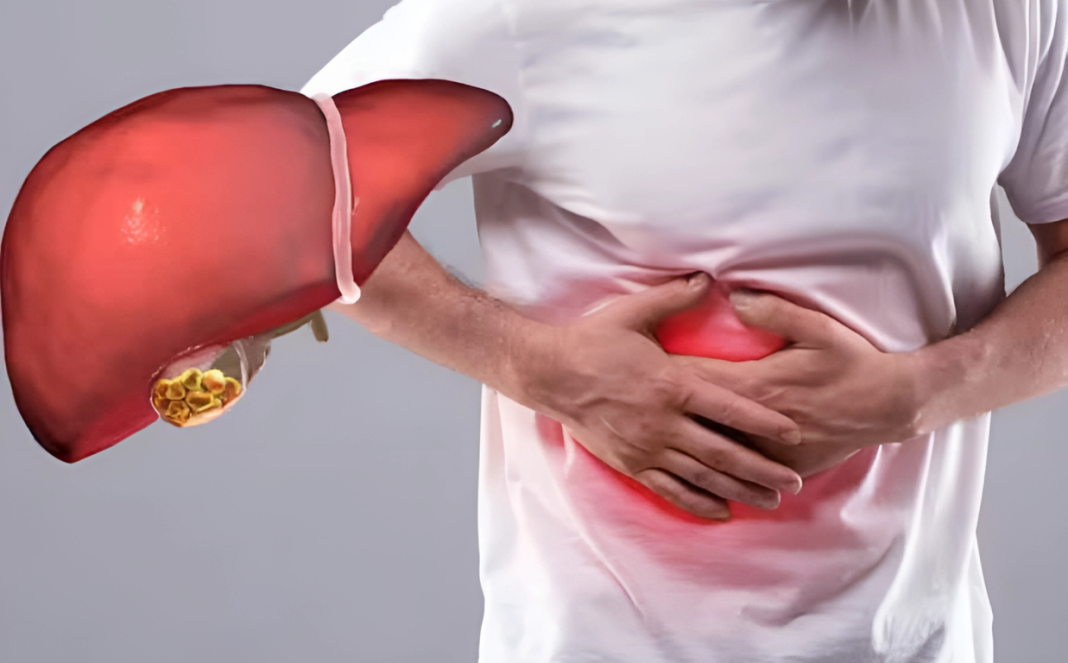
Fat Accumulation in the Liver Without Alcohol: A Growing Concern
Non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) is rapidly becoming a primary global health concern. Recent studies indicate that 25% to 35% of the world’s population is affected by this condition, with the numbers significantly higher in India. Shockingly, even individuals who abstain from alcohol consumption are at risk of developing this disease, leading to severe health complications over time.
Lack of Awareness Delays Treatment
Many people are unaware that fat can accumulate in the liver gradually, even in the absence of alcohol consumption. Due to this lack of awareness, diagnosis and treatment are often delayed, exacerbating the problem. Liver diseases, especially fatty liver, are on the rise, prompting the Union Health Ministry to issue awareness guidelines on NAFLD. Studies suggest that at least 3 out of every 10 people in India suffer from this condition, making it a critical public health issue.
NAFLD: The Silent Killer
A study presented at the annual conference of the Endocrine Society in Chicago highlights the alarming increase in NAFLD cases. More well-known conditions like diabetes often overshadow this disease, yet it poses equally severe health risks. The World Health Organization (WHO) has already labeled India the “diabetes capital of the world,” and the prevalence of NAFLD further intensifies the country’s healthcare challenges.
Understanding Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD)
NAFLD is a type of metabolic dysfunction that occurs when the body fails to digest food properly, leading to toxin accumulation. This increases harmful cholesterol levels and triglycerides, resulting in excess fat storage in the liver. When fat accumulation becomes excessive, it can cause liver inflammation, scarring (cirrhosis), and even liver cancer.
Why is NAFLD Prevalent in India?
Several factors contribute to the rising cases of NAFLD in India:
- Dietary Habits: Indian cuisine is rich in oil, spices, and fats, which increases the risk of fatty liver.
- Low Digestive Efficiency: Many individuals have poor digestion compared to the high consumption of fatty foods.
- Sedentary Lifestyle: A lack of regular exercise contributes to metabolic disorders.
- Uncontrolled Eating Habits: Frequent consumption of processed foods, sugary snacks, and high-calorie meals further worsens liver health.
Consequences of Fatty Liver Disease
If left untreated, NAFLD can progress to severe complications such as:
- Liver inflammation and fibrosis
- Cirrhosis, which causes permanent liver damage
- Increased risk of liver cancer
- Higher chances of developing diabetes and cardiovascular diseases
How to Prevent and Manage NAFLD
Dr. Arunanshu Talukdar, a medical expert, emphasizes that while excessive alcohol consumption is a known cause of liver disease, poor eating habits, and an unhealthy lifestyle also play a significant role in NAFLD development. Early detection can help manage the condition effectively. Here are some key prevention strategies:
1. Maintain a Healthy Weight
Excess body fat increases the risk of NAFLD. Aim for gradual weight loss through a balanced diet and physical activity.
2. Adopt a Liver-Friendly Diet
- Reduce intake of oily, fried, and processed foods
- Limit sugar, refined carbohydrates, and high-fat dairy products
- Increase fiber-rich foods like fruits, vegetables, and whole grains
- Include lean proteins, nuts, and healthy fats (such as olive oil)
3. Engage in Regular Exercise
Physical activity helps burn excess fat and improve metabolism. Combining aerobic exercises and strength training is beneficial for overall liver health.
4. Limit Caloric Intake
Portion control and mindful eating can help prevent excessive fat accumulation in the liver.
5. Monitor Liver Health Regularly
Routine health check-ups, including liver function tests and ultrasound scans, can detect early signs of NAFLD and prevent complications.
Recognizing the Symptoms of NAFLD
NAFLD often goes unnoticed in its early stages, but some warning signs include:
- Increased appetite and cravings for fried foods and sweets
- Unexplained weight gain
- Yellowish urine and jaundice-like symptoms
- Persistent fatigue and weakness
Conclusion
NAFLD is a growing health concern, particularly in India, where diet and lifestyle choices significantly contribute to its prevalence. Raising awareness, making dietary modifications, and adopting a healthier lifestyle can help prevent and manage this silent epidemic. Early detection and proactive measures ensure liver health and prevent life-threatening complications.